1. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
Obstacles and protruding elements in the path of travel.
Low overhanging signs.
Lack of warning signs around obstructions.
2. PLANNING PRINCIPLE
To design a barrier-free path for the safety and independence of disabled people,
especially the sightless.
3. DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
3.1 General
 Obstructions include street furniture,
traffic signs, direction signs, street plans, bollards, plants, trees, shop awnings and
advertising signs, etc. Obstructions include street furniture,
traffic signs, direction signs, street plans, bollards, plants, trees, shop awnings and
advertising signs, etc.
 Obstructions should be placed outside the
path of travel wherever possible. Obstructions should be placed outside the
path of travel wherever possible.
 Obstructions in the pathway should be easy to
detect, and if possible, should be placed along one continuous line. Obstructions in the pathway should be easy to
detect, and if possible, should be placed along one continuous line.
 Protruding elements should be avoided. Protruding elements should be avoided.
 The minimum width of a clear unobstructed
path should be 0.90 m. The minimum width of a clear unobstructed
path should be 0.90 m.
3.2 Obstructions on the pathway surface
 Obstructions on the pathway surface should
have one of the following design features in order to be detected by the cane of a
sightless person: Obstructions on the pathway surface should
have one of the following design features in order to be detected by the cane of a
sightless person:
(a) A straight shape rising from the pathway surface (fig. 1).
(b) A 0.10 m raised platform (fig. 2).
(c) Tactile warning markings on the ground around the obstruction. The warning markings
should extend over a width of at least 0.60 m outside the projected area at the base of
the obstacle (fig. 3).
3.3 Overhanging obstructions
 Overhanging signs in accessible pathways
should be mounted at a minimum clear height of 2.00m to allow a sightless person to pass
safely (fig. 4). Overhanging signs in accessible pathways
should be mounted at a minimum clear height of 2.00m to allow a sightless person to pass
safely (fig. 4).
 Overhanging vegetation should be clipped to a
minimum clear height of 2.00 m (fig. 5). Overhanging vegetation should be clipped to a
minimum clear height of 2.00 m (fig. 5).
 Undetectable obstacles mounted lower than
2.00 m may project a maximum distance of 0.10m into the pathway. Otherwise they should be
recessed or covered (fig. 6). Undetectable obstacles mounted lower than
2.00 m may project a maximum distance of 0.10m into the pathway. Otherwise they should be
recessed or covered (fig. 6).
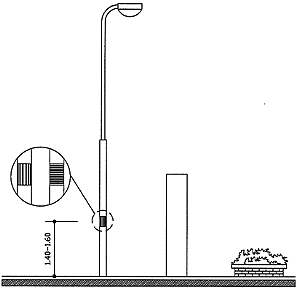
3.4 Fixed poles
 Fixed poles should have contrasting durable
colour marking strips of at least 0.30 m in length, placed with the centre line at a
height between 1.40 m and 1.60 m, to warn pedestrians with limited vision (fig. 1). Fixed poles should have contrasting durable
colour marking strips of at least 0.30 m in length, placed with the centre line at a
height between 1.40 m and 1.60 m, to warn pedestrians with limited vision (fig. 1).
3.5 Garbage bins
 Garbage bins attached to lampposts should not
face the line of pedestrian flow so as to minimize collisions and should be painted in a
contrasting colour so that people with limited vision may easily identify them (fig. 7). Garbage bins attached to lampposts should not
face the line of pedestrian flow so as to minimize collisions and should be painted in a
contrasting colour so that people with limited vision may easily identify them (fig. 7).
3.6 Spaces below ramps and stairs
 Spaces below ramps and stairs should be
blocked out completely by protective rails or raised curbs or marked with a tactile
surface (fig. 8). Spaces below ramps and stairs should be
blocked out completely by protective rails or raised curbs or marked with a tactile
surface (fig. 8).
3.7 Bicycle stands
 Bicycle stands should be located on a raised
platform. Bicycle stands should be located on a raised
platform.
3.8 Wires
 Stabilizing wires and wire netting should be
painted in a contrasting colour or blocked out. 3.9 Bollards (1) (fig. 9) Stabilizing wires and wire netting should be
painted in a contrasting colour or blocked out. 3.9 Bollards (1) (fig. 9)
 Bollards should be painted in a contrasting
colour or in coloured stripes. Bollards should be painted in a contrasting
colour or in coloured stripes.
 The distance between guiding posts should be
around 1.20 m. The distance between guiding posts should be
around 1.20 m.
3.10 Roadworks
 Excavations and roadworks form temporary
obstructions within the route of travel. They should be protected by easily detected
continuous barriers, scaffolding, and fences for safety reasons. Excavations and roadworks form temporary
obstructions within the route of travel. They should be protected by easily detected
continuous barriers, scaffolding, and fences for safety reasons.
 Barriers should be identified by stripped
colour markings and should be lit at night, to guide people with limited vision. Barriers should be identified by stripped
colour markings and should be lit at night, to guide people with limited vision.
 The barrier height should be between 0.75 m
and and 0.95 m. The distance between the bottom of the barrier and the pathway surface
should not exceed 0.10 m. The barrier height should be between 0.75 m
and and 0.95 m. The distance between the bottom of the barrier and the pathway surface
should not exceed 0.10 m.
4. EXISTING CONSTRUCTIONS
 Existing obstructions within the path of
travel should be redesigned to conform to all the above requirements Existing obstructions within the path of
travel should be redesigned to conform to all the above requirements
Notes:
(1) Bollards or guard posts are placed to keep out undesired motor traffic from pedestrian
areas or to indicate a non parking area. |