1. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
Unsafe railings.
Hard to grip handrails.
No railings or handrails.
2. PLANNING PRINCIPLE
To install adequate railing, wherever needed for the comfort and safety of all people,
especially those with mobility problems.
3. DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
3.1 General
 Safety guards or railings should be installed
around hazardous areas, stairs, ramps, accessible roofs, mezzanines, galleries, balconies
and raised platforms more than 0.40 m high. Safety guards or railings should be installed
around hazardous areas, stairs, ramps, accessible roofs, mezzanines, galleries, balconies
and raised platforms more than 0.40 m high.
 On stairways, windows positioned less than
1.00 m from the landing should have railings. On stairways, windows positioned less than
1.00 m from the landing should have railings.
 Handrails should be installed to assist
disabled persons in bathrooms and toilets (see Rest Rooms). Handrails should be installed to assist
disabled persons in bathrooms and toilets (see Rest Rooms).
 Spacing between the vertical and horizontal
bars of railings should be narrow for the safety of children. Spacing between the vertical and horizontal
bars of railings should be narrow for the safety of children.
 Handrails should not obstruct the path of
travel. Handrails should not obstruct the path of
travel.
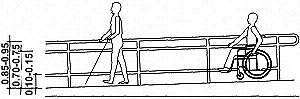
3.2 Height (fig. 1) (1)
 To facilitate use by ambulant disabled and
elderly people, handrails should be mounted between 0.85 m and 0.95 m above the finished
floor level. To facilitate use by ambulant disabled and
elderly people, handrails should be mounted between 0.85 m and 0.95 m above the finished
floor level.
 For the benefit of wheelchair users, a second
handrail can be mounted between 0.70 m and 0.75 m from the floor. For the benefit of wheelchair users, a second
handrail can be mounted between 0.70 m and 0.75 m from the floor.
 To facilitate use by children and short
people, a third handrail can be mounted at a height of 0.60 m. To facilitate use by children and short
people, a third handrail can be mounted at a height of 0.60 m.
 To guide sightless people using a long cane,
a rail should be mounted at a height between 0.10 m and 0.15 m (fig. 1); or a low curb
should be installed at a height between 50 mm and 75 mm (fig. 2). Low curbs also act as
wheelstops. To guide sightless people using a long cane,
a rail should be mounted at a height between 0.10 m and 0.15 m (fig. 1); or a low curb
should be installed at a height between 50 mm and 75 mm (fig. 2). Low curbs also act as
wheelstops.
3.3 Mounting
 Railings should be securely attached to the
wall or to a supporting structure so as to withstand heavy loads. Railings should be securely attached to the
wall or to a supporting structure so as to withstand heavy loads.
 Railings should not end abruptly but extend
to the floor or blend into the wall so as not to create a hazard for sightless people. Railings should not end abruptly but extend
to the floor or blend into the wall so as not to create a hazard for sightless people.
3.4 Form (fig. 3)
 Handrails should allow a firm and easy grip. Handrails should allow a firm and easy grip.
 Circular cross-sections with a diameter of 40
mm are preferable. Circular cross-sections with a diameter of 40
mm are preferable.
 Sharp edges should be avoided. Sharp edges should be avoided.
3.5 Handrails for ramps and stairs
 Handrails should continue uninterrupted
(except for doorways) on both sides and around the landing. Handrails should continue uninterrupted
(except for doorways) on both sides and around the landing.
 Handrails should extend horizontally for a
distance between 0.30 m and 0.45 m at the top and bottom of stairs and ramps, except in
places where extensions could obstruct the pedestrian flow (fig.4). Handrails should extend horizontally for a
distance between 0.30 m and 0.45 m at the top and bottom of stairs and ramps, except in
places where extensions could obstruct the pedestrian flow (fig.4).
 For stairs or ramps more than 3.00 m wide, a
continuous intermediate handrail could be provided (see Ramps; Stairs). For stairs or ramps more than 3.00 m wide, a
continuous intermediate handrail could be provided (see Ramps; Stairs).
3.6 Wall-mounted handrails
 The space between the handrail and the wall
should be between 40 mm and 50 mm for smooth walls and 60 mm for rough textured walls
(fig. 5). The space between the handrail and the wall
should be between 40 mm and 50 mm for smooth walls and 60 mm for rough textured walls
(fig. 5).
 Where handrails are fully recessed into
walls, a space of at least 0.15 m should be allowed between the top of the rail and the
top of the recess (fig. 6). Where handrails are fully recessed into
walls, a space of at least 0.15 m should be allowed between the top of the rail and the
top of the recess (fig. 6).
3.7 Tactile marking
 For emergency exit stairs or ramps, a
contrasting tactile strip at least 0.90 m long should be applied to the top and bottom
edges of the handrail to alert the partially sighted. For emergency exit stairs or ramps, a
contrasting tactile strip at least 0.90 m long should be applied to the top and bottom
edges of the handrail to alert the partially sighted.
3.8 Colour
 A contrasting colour is recommended for
handrails to alert people with sight problems. A contrasting colour is recommended for
handrails to alert people with sight problems.
4. EXISTING CONSTRUCTIONS
 If existing railings and handrails do not
comply with the above requirements, they should be modified or replaced. If existing railings and handrails do not
comply with the above requirements, they should be modified or replaced.
Notes:
(1) Measurements are taken from the front of the tread. |