- ON THE DECADE
- THE DECADE'S CAMPAIGN
- REPORTING ON PROGRESS
- THE DECADE'S PROGRAMMES
- FOCUS AREAS
-
- Access to sanitation
- Financing water
- Gender and water
- Human right to water
- Integrated Water Resources Management
- Transboundary waters
- Water and cities
- Water and energy
- Water and food security
- Water and sustainable development
- Water and the green economy
- Water cooperation
- Water quality
- Water scarcity
- FOCUS REGIONS
- RESOURCES FOR
- UN e-RESOURCES
Transboundary waters
As water quality degrades or the quantity available has to meet rising demands over time, competition among water users intensifies. This is nowhere more destabilizing than in river basins that cross political boundaries. But experience shows that in many situations, rather than causing open conflict, the need for water sharing can generate unexpected cooperation.
Despite the complexity of the problems, records show that water disputes can be handled diplomatically. The last 50 years have seen only 37 acute disputes involving violence, compared to 150 treaties that have been signed. Nations value these agreements because they make international relations over water more stable and predictable. In fact, the history of international water treaties dates as far back as 2500 BC, when the two Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma crafted an agreement ending a water dispute along the Tigris River - often said to be the first treaty of any kind. Since then, a large body of water treaties has emerged. According to the Food and Agricultural Organization, more than 3,600 treaties related to international water resources have been drawn up since 805 AD. The majority of these deal with navigation and boundary demarcation. The focus of negotiation and treaty-making in the last century has shifted away from navigation towards the use, development, protection and conservation of water resources.
Legal agreements on water sharing have been negotiated and maintained even as conflicts have persisted over other issues. Cambodia, Laos, Thailand and Vietnam, have been able to cooperate since 1957 within the framework of the Mekong River Commission, and they had technical exchanges throughout the Vietnam War. Since 1955 Israel and Jordan, have held regular talks on the sharing of the Jordan River, even as they were until recently in a legal state of war. The Indus River Commission survived two wars between India and Pakistan. A framework for the Nile River Basin, home to 160 million people and shared among 10 countries, was agreed in February 1999 in order to fight poverty and spur economic development in the region by promoting equitable use of, and benefits from, common water resources. The nine Niger River Basin countries have agreed on a framework for a similar partnership. These cases reflect two important elements of international water resources cooperation: the need for an institution to effectively develop a process of engagement over time; and well-funded third-party support trusted by all factions.
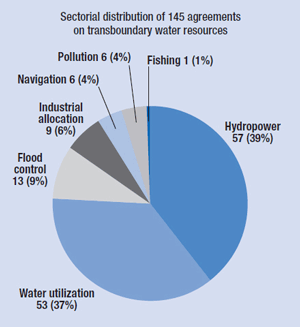
Source: Human Development Report 2006. Beyond scarcity: Power, poverty and the global water crisis. Chapter 6. UNDP, 2006
The more than 3,600 agreements and treaties signed are an achievement in themselves, but a closer look at them still reveals significant weaknesses. What is needed are workable monitoring provisions, enforcement mechanisms, and specific water allocation provisions that address variations in water flow and changing needs. The 1997 United Nations Convention on Non-Navigational Uses of International Watercourses is one international instrument that specifically focuses on shared water resources. It established two key principles to guide the conduct of nations regarding shared watercourses: "equitable and reasonable use" and "the obligation not to cause significant harm" to neighbours. However, it is up to countries themselves to spell out precisely what these terms mean in their watersheds.
There is a consensus among experts that international watercourse agreements need to be more concrete, setting out measures to enforce treaties made and incorporating detailed conflict resolution mechanisms in case disputes erupt. Better cooperation also entails identifying clear yet flexible water allocations and water quality standards, taking into account hydrological events, changing basin dynamics and societal values.
Sources:
- Water Without Borders. Backgrounder. United Nations Department of Public Information, 2004
- Human Development Report 2006. Beyond scarcity: Power, poverty and the global water crisis. Chapter 6. UNDP, 2006.
Did you know?
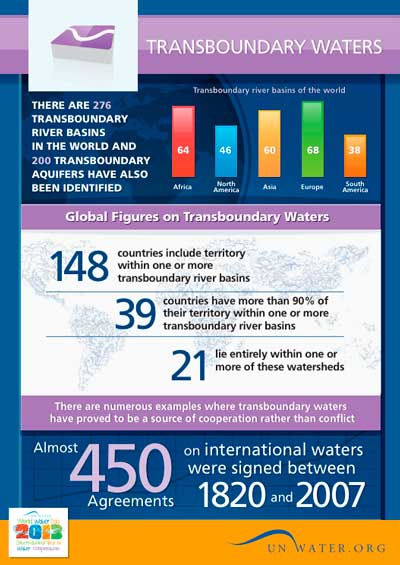
- The world's 263 transboundary lake and river basins cover nearly half of the Earth's land surface.
- A total of 145 nations include territory within international basins, and 21 countries lie entirely within international basins.
- While most basins are shared between just two countries, there are many basins where this number is much higher. There are 13 basins worldwide that are shared between 5 and 8 riparian nations. Five basins, the Congo, Niger, Nile, Rhine and Zambezi, are shared between 9 and 11 countries. The river that flows through the most nations is the Danube, which travels within the territory of 18 nations.
UN initiatives that are helping to raise the issue...
- UN General Assembly Resolution on the Law of Transboundary Aquifers
The 63rd session of the UN General Assembly adopted Resolution A/RES/63/124 on the Law of Transboundary Aquifers by consensus on 11 December 2011. The resolution encourages States 'to make appropriate bilateral or regional arrangements for the proper management of their transboundary aquifers, taking into account the provisions of these draft articles', which are annexed to the resolution. These provisions include cooperation among States to prevent, reduce and control pollution of shared aquifers. In view of the importance of these 'invisible resources', States are invited to consider these draft articles as a basis for the elaboration of a convention. The Law of Transboundary Aquifers is a concrete step forward towards the peaceful sharing of groundwater resources. Until then there was no instrument of international law that could provide a complete set of recommendations and guidelines for the sustainable and peaceful management of transboundary aquifers. - 2013: International Year of Water Cooperation
In February 2011, the UN General Assembly decided to proclaim 2013 International Year of Water Cooperation. - Convention on the Law of the Non-Navigational Uses of International Watercourses
The 1997 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Non-Navigational Uses of International Watercourses is the only treaty governing shared freshwater resources that is of universal applicability. It is a framework convention, in the sense that it provides a framework of principles and rules that may be applied and adjusted to suit the characteristics of particular international watercourses. Some key guiding principles set out in the document include: the equitable and reasonable utilization of international watercourses; the application of appropriate measures to prevent harm to other States sharing an international watercourse; and the principle of prior notification of planned measures. For the Convention to become legally binding, at least 35 nations must ratify it. - World Water Day 2009: Shared Waters, Shared Opportunities
World Water Day 2009 was dedicated to the theme "Shared Waters, Shared Opportunities". The focus was placed on transboundary waters and on the fact that nurturing the opportunities for cooperation in transboundary water management can help build mutual respect, understanding and trust among countries and promote peace, security and sustainable economic growth. - UN-Water Thematic Priority Area on Transboundary Waters
The UN-Water Thematic Priority Area (TPA) on Transboundary Waters is intended to provide a platform to promote coherence and coordination of activities by UN-Water Members and Partners in the area of transboundary waters. It does this by facilitating a steady exchange of information, experiences and lessons learned and by promoting joint efforts.
To know more
 Model Provisions on Transboundary Groundwaters
Model Provisions on Transboundary Groundwaters
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). February 2014
This document provides specific non-binding guidance for the implementation of the Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes (Water Convention) with regard to groundwater and facilitating the application of the principles of the Convention to transboundary groundwaters. The document comprises an introduction followed by nine model provisions, each accompanied by commentary. The Model Provisions reflect the current state of international water law with regard to transboundary groundwaters and also show, in the commentaries, the practical ways and examples of its application in inter-State practice. The Model Provisions are designed to benefit Governments, interested stakeholders and both Parties and non-Parties to the Water Convention.
 Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes
Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). January 2014
This convention, which was adopted in 1992 and entered into force in 1996, serves as a mechanism to strengthen international cooperation and national measures for the ecologically sound management and protection of transboundary surface waters and groundwaters. Furthermore, it provides an intergovernmental platform for the day-to-day development of transboundary cooperation. The Convention is open to all United Nations Member States. This document describes the amendments to the Convention with definitions of its structure and intentions in English, French and Russian.
 (The) Global Opening of the 1992 Water Convention
(The) Global Opening of the 1992 Water Convention
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). October 2013
The Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes (Water Convention) was adopted in 1992 and entered into force in 1996. This publication explains the obligations under the Water Convention and the way in which its institutional platform works, as well as the advantages for the States to become Party to the Water Convention. It also addresses the relationship between the Water Convention and the 1997 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Non-navigational Uses of the International Watercourses. The publication is intended for future Parties, international partners, non-governmental organizations and academia, and aims to strengthen the understanding of the Water Convention and its global opening to all United Nations Member States.
 Science-Policy Bridges Over Troubled Waters. Making Science Deliver Greater Impacts in Shared Water Systems. Synthesis Report
Science-Policy Bridges Over Troubled Waters. Making Science Deliver Greater Impacts in Shared Water Systems. Synthesis Report
Global Environmental Facility (GEF), United Nations University Institute for Water, Environment and Health (UNU-INWEH). September 2012
This report serves to provide a global perspective on the state of challenges and pressures facing transboundary water systems, both freshwater and marine. The context of this Synthesis is the need and effective use of science to address these challenges and the translation of such science use to policy for multi-country management of shared water resources. The report brings together the findings and efforts of the International Waters (IW) System Type Working Groups on groundwater, lakes, rivers, land-based pollution sources and, large marine ecosystems and the open ocean.
International Waters: Review of Legal and Institutional Frameworks
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Global Environment Facility (GEF), UBC. April 2012
This report discusses the legal and institutional frameworks that apply to 28 international water bodies that were identified as part of the UNDP-GEF project on "Good Practices and Portfolio Learning in GEF Transboundary Freshwater and Marine Legal and Institutional Frameworks". The analysis in this report is organized by a common set of eighteen criteria and is intended to provide information that can be used to support further research and analysis, with the ultimate goal of identifying a set of common elements of good governance for transboundary freshwater and marine water bodies as well as groundwater systems. This report is based on primary materials that establish legal and institutional frameworks, such as international agreements (including treaties and conventions where applicable), protocols or action plans. Where relevant secondary materials were available (primarily for water bodies with more extensive legal frameworks).
 Reader on Transboundary Water Cooperation [
Reader on Transboundary Water Cooperation [ - 164 KB]
- 164 KB]
UN-Water Decade Programme on Advocacy and Communication (UNW-DPAC). 2010
This reader is intended for all those interested in getting familiar with transboundary water issues. The reader provides basic references for easy reading and some of the latest and most relevant United Nations publications on transboundary water and cooperation issues. It also contains experiences from different regions of the world. Link is provided when the publication is available online.
 Atlas of Transboundary Aquifers. Global maps, regional cooperation and local inventories
Atlas of Transboundary Aquifers. Global maps, regional cooperation and local inventories
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). 2009
This atlas presents a compilation of data from more than 200 transboundary aquifers that have been identified in the Americas, Asia, Africa, South-Eastern Europe, Central Asia and Caucasus, and Middle East. The Atlas also provides a factual backdrop to the recent Resolution of the UN General Assembly on the Law of Transboundary Aquifers. While the atlas serves to provide reference information, it also demonstrates the outcome of successful cooperation among countries in together compiling joint interpretations of their hydrogeological information.
 Transboundary waters: Sharing Benefits, Sharing Responsibilities [
Transboundary waters: Sharing Benefits, Sharing Responsibilities [ - 14.1 MB]
- 14.1 MB]
UN-Water. 2008
This UN-Water thematic paper presents the main benefits of transboundary water cooperation and the basic pillars considered as necessary for long-term, sustainable and reliable transboundary cooperation. The paper also introduces the role of UN-Water in this field as well as the work of the different UN agencies on transboundary water cooperation.
 Transboundary water resources management: The Role of International Watercourse Agreements in Implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity [
Transboundary water resources management: The Role of International Watercourse Agreements in Implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity [ - 924 KB]
- 924 KB]
Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (UNCBD). 2008
This document explains why biodiversity conservation and sustainable use present a powerful argument to manage transboundary waters better, how regulatory frameworks to achieve this can be improved and why doing so fulfils commitments made under the Convention on Biological Diversity.
 2nd United Nations World Water Development Report: Water, a Shared Responsibility. Chapter 11 [
2nd United Nations World Water Development Report: Water, a Shared Responsibility. Chapter 11 [ - 704 KB]
- 704 KB]
UN World Water Assessment Programme (WWAP). 2006
The United Nations World Water Development Report, released every three years, provides a mechanism for monitoring changes in the resource and its management and tracking progress towards achieving targets, particularly those of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and the World Summit on Sustainable Development. Chapter 11 of the 2nd edition of the UN World Water Development Report focuses on the dynamics of cooperation and highlights mechanisms and indicators for cooperation and shared governance of transboundary waters.
 Human Development Report 2006. Beyond scarcity: Power, poverty and the global water crisis. Chapter 6
Human Development Report 2006. Beyond scarcity: Power, poverty and the global water crisis. Chapter 6
[ - 1.02 MB]
- 1.02 MB]
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). 2006
The Human Development Report was first launched in 1990 with the goal of putting people back at the center of the development process in terms of economic debate, policy and advocacy. Each report focuses on a highly topical theme in the current development debate, providing path-breaking analysis and policy recommendations. Chapter 6 of the Human Development Report 2006 focuses on transboundary waters management related issues.
 History and Future of Shared Water Resources
History and Future of Shared Water Resources
[ - 3.13 MB]
- 3.13 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
This publication contains a number of "think pieces" which analyze historical experiences from the distant past of prehistory to the present, and identify the means for dealing with the relative scarcity of water created by increasing demands relative to water available when and where it is needed. They also investigate the causes of the prevailing perceptions of water scarcity and the propagation of the idea that future wars will be fought about water. These studies helped in assessing the future of shared water resources and can serve as a basis for future planning.
 International Waters: Indicators for Identifying Basins at Risk [
International Waters: Indicators for Identifying Basins at Risk [ - 1.19 MB]
- 1.19 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
This publication assess all reported events of either conflict or cooperation between nations over water resources over the last fifty years and use these events to inform the identification of basins at greatest risk of dispute in the near future (five to ten years). The study is divided into two components: (a) compilation and assessment of relevant biophysical, socioeconomic, and geopolitical data in a global Geographic Information System (GIS), and use of these factors to determine history-based indicators for future tensions along international waterways, (b) using these indicators, identification of basins at risk for the coming decade.
International agreements and law
 Guide to Implementing the Water Convention
Guide to Implementing the Water Convention
Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). September 2013
The Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes (Water Convention) was adopted in 1992 and entered into force in 1996. It brings together almost all countries sharing transboundary waters in the pan-European region, and is expected to achieve broader participation with its global opening to all United Nations Member States. This Guide constitutes a commentary to the Convention’s provisions, providing explanations of the legal, procedural, administrative, technical and practical aspects of the Convention’s requirements for appropriate implementation. It aims to strengthen the understanding of the Convention among current and future Parties, international partners, non-governmental organizations and academia.
 Freshwater and International Law: The Interplay between Universal, Regional and Basin Perspectives
Freshwater and International Law: The Interplay between Universal, Regional and Basin Perspectives
[ - 472.52 KB]
- 472.52 KB]
UN World Water Assessment Programme (WWAP). 2009
This paper focuses on some of the characteristics of the latest developments concerning international freshwater resources law by looking at the interplay of norms adopted at three levels where important new instruments have been adopted: the universal, regional and basin levels. The first part of the paper focuses on instruments adopted at the universal level, such as the United Nations Convention on the Law of Non-Navigational Uses of International Watercourses and the International Law Commission Draft Articles on the Law of Transboundary Aquifers. The second part deals with the development of laws at the regional and basin levels.
 Transboundary aquifers: managing a vital resource. The UNILC draft articles on the law of transboundary aquifers [
Transboundary aquifers: managing a vital resource. The UNILC draft articles on the law of transboundary aquifers [ - 870.51 KB]
- 870.51 KB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). 2009
The UN International Law Commission (UNILC) embarked on the codification of the law of transboundary aquifers in 2002 in order to provide a legal regime for the proper management of aquifers. This brochure aims at improving the understanding of transboundary aquifers and the importance of their role in water governance and thus the drafting and implementation of the Convention on Transboundary Aquifers.
Groundwater in international law. Compilation of treaties and other legal instruments [ - 503 KB]
- 503 KB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). 2005
This publication brings together a variety of binding and non-binding international law instruments that, in varying degrees and from different angles, deal with groundwater. Its aim is to report developments in international law and to contribute to detecting law in the making in this field.
 Transforming Potential Conflict into Cooperation Potential: The Role of International Water Law
Transforming Potential Conflict into Cooperation Potential: The Role of International Water Law
[ - 1.49 MB]
- 1.49 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
This study discusses the relevance and role of international water law in the promotion of cooperation over shared transboundary watercourses. With its focus on actual case studies and through examination of contemporary state practice and detailed analysis of the UN Watercourses Convention, this work aims to provide water resource experts from all disciplines with an overview of the rules of international law that govern interstate relations over water.
 Institutions for international freshwater management
Institutions for international freshwater management
[ - 809 KB]
- 809 KB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
This report describes selected bi- and multilateral institutions for the management of international river basins, lakes, and aquifers. It provides comparative information on various institutional aspects such as scope of authority, internal structure, decision-making procedures, and dispute settlement mechanisms.
 Conflict and Cooperation in the Management of International Freshwater Resources: A Global Review
Conflict and Cooperation in the Management of International Freshwater Resources: A Global Review
[ - 1.41 MB]
- 1.41 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
This report aims to identify the state of the art concerning conflict and cooperation in managing international freshwaters. Its more specific objects are the following: (a) to complement the in-depth case studies prepared by the UNESCO "From Potential Conflict to Cooperation Potential" (PCCP) project by a more in-breadth coverage of international freshwater management, (b) to show the wide variety of issues, contexts, and solutions chosen, (c) to identify general "lessons" on conflict prevention/resolution and cooperation.
Atlas of International Freshwater Agreements
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Oregon State University. 2002
This atlas contains an historical overview of international river basin management; a detailed listing of more than 300 international freshwater agreements; and a collection of thematic maps related to the agreements, their content, and the river basins they represent.
Experiences from around the world
Americas
 International Management in the Columbia River System [
International Management in the Columbia River System [ - 944.4 KB]
- 944.4 KB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
This document presents an overview of selected physical, human phenomena and international water management issues in the Columbia River system.
 The Case of the Trifinio Plan in the Upper Lempa: Opportunities and Challenges for the Shared Management of Central American Transnational Basins
The Case of the Trifinio Plan in the Upper Lempa: Opportunities and Challenges for the Shared Management of Central American Transnational Basins
[ - 562.87 KB]
- 562.87 KB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
The upper watershed of the Lempa River is shared by Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras, as outlined in the Trifinio Plan. Its management represents a novel experience for Central America. It reveals the advances made in the management of the natural resources of a trans-national watershed, through the political will of the countries at the highest level, institutionalized through an international treaty, making way for a new form of organizational management.
 Co-operation on the lake Titicaca [
Co-operation on the lake Titicaca [ - 35.12 MB]
- 35.12 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2006
This case study begins with a characterization of the region in terms of socioeconomic, hydrological, geographical and meteorological data. This is followed by a historical overview of the actions undertaken to achieve a common governmental approach to the problem of the shared use of hydrological and hydrobiological resources. Finally, topics related to the elaboration of the Peru-Bolivia TDPS System Master Plan, and to the creation and functioning of the Lake Titicaca Binational Autonomous Authority (ALT) are presented, stating in detail the main actions carried out. The study is, above all, an appraisal of the experience acquired as a result of the achievements made in the joint management of the Lake Titicaca Basin, and analyses the ALTs relationship with other local institutions. It also discusses the perception of the ALT that authorities from both countries points of view. The study closes with conclusions and recommendations on the subject.
Asia
 Vulnerability Assessment of Freshwater Resources to Climate Change: Implications for Shared Water Resources in the West Asia Region
Vulnerability Assessment of Freshwater Resources to Climate Change: Implications for Shared Water Resources in the West Asia Region
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). 2012
Asia countries have been experiencing different degrees of natural and anthropogenic water risk affecting the sustainability of their limited water resources and preservation of the ecosystem equilibrium. The fragile arid environment and its resiliency to cope with external natural and anthropogenic activities, including the expected impacts of climate change, present a major challenge to decision-makers who must achieve adequate, safe and dependable water and food supply in the future to improve human well-being in their societies, and to meet the requirements of future generations. This document provides a useful tool for decision-makers to identify potential risks to freshwater resources in the region from the impacts of climate change. The overall objective of this study is to carry out a national and regional vulnerability assessment of freshwater resources to better understand the existing status of water under the prevailing conditions and to ascertain the most dominant factors that influence vulnerability.
 Regional Water Intelligence Report Central Asia. Baseline Report [
Regional Water Intelligence Report Central Asia. Baseline Report [ - 874.53 KB]
- 874.53 KB]
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI). 2010
The purpose of Regional Water Intelligence Reports (RWIR) is to provide regular updates on the political economy of transboundary water resources issues, management and development in support of sustainable investments. The RWIR focus on the socio-economic aspects of water management and highlight the links between water, energy, food and human security from a regional perspective.
Shared Waters - Shared Opportunities. World Water Day March 22. Transboundary Waters in the ESCWA Region [ - 1.19 MB]
- 1.19 MB]
United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia (UNESCWA). 2009
This fact sheet outlines the general principles of international water law and the major international conventions on shared water; it also delineates the major transboundary river basins and shared water aquifers in the ESCWA region.
Regional cooperation between countries in the management of shared water resources: Case studies of some countries in the ESCWA region [ – 320.14 KB]
– 320.14 KB]
United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia (UNESCWA). 2005
This report presents two case studies on shared water resources in the ESCWA region. Part one presents a study of the Al-Kabeer Al-Janoubi river shared by Lebanon and the Syrian Arab Republic. Part two presents a study of the basalt aquifer shared by Jordan and the Syrian Arab Republic.
 Past Experience and Future Challenges: Cooperation in Shared Water Resources in Central Asia
Past Experience and Future Challenges: Cooperation in Shared Water Resources in Central Asia
Asian Development Bank (ADB). 2004
This publication compiles the proceedings of the Regional Consultation Workshop on Cooperation in Shared Water Resources in Central Asia: Past Experience and Future Challenges, which was held in Almaty, Kazakhstan, from 26 to 28 September 2002. The proceedings present different cooperation experiences between Central Asian countries and provide some recommendations to enhance transboundary water management.
 Jordan Case Study [
Jordan Case Study [ - 1.39 MB]
- 1.39 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
This case study is divided into two parts. Part 1 analyzes water conflict and negotiated resolution issues and Part 2 presents the negotiations and the water agreement between the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan and the State of Israel.
 Mekong Case Study [
Mekong Case Study [ - 1.44 MB]
- 1.44 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
This Mekong case study focuses mainly on the Lower Mekong Basin and its upper part in the Yunnan Province of China. It provides information about the historical context, legal aspects, frameworks for negotiation and mediation, and system analysis. The study is aimed at reviewing lessons learnt and providing possible best practices for international river basins management.
 Lessons on Cooperation Building to Manage Water Conflicts in the Aral Sea Basin [
Lessons on Cooperation Building to Manage Water Conflicts in the Aral Sea Basin [ - 1.51 MB]
- 1.51 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
This case study presents the current situation of the Aral Sea Basin and lessons to be learned from the difficult and complex conditions that followed the break-up of the Soviet Union. That collapse led to an intricate environmental problem, and the countries of the basin are working through cooperation to find an effective way to manage water resources.
Transboundary water cooperation in the newly independent States [ - 567.76 KB]
- 567.76 KB]
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). 2003
This document aims to define the status, trends and further needs with regard to the transboundary water cooperation in the newly independent States (NIS), and between NIS and other neighbouring countries.
Africa
 Sharing the Incomati Waters: Cooperation and Competition in the Balance [
Sharing the Incomati Waters: Cooperation and Competition in the Balance [ - 2.75 MB]
- 2.75 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
This case study deals with the Incomati river basin, which is relatively small but has some interesting features, both in terms of socio-political developments and water use. The case study presents information about the natural characteristics of the basin, its political history, water developments, the legal framework, and the negotiations that took place during the period 1964-2002.
 The Nile: Moving Beyond Cooperation [
The Nile: Moving Beyond Cooperation [ - 1.06 MB]
- 1.06 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003 This paper examines the development of cooperation on the River Nile. The paper outlines key aspects of the Nile Basin's history, geography and politics before looking at some of the legal, socioeconomic and development challenges that lie ahead.
Europe
 Second Assessment of Transboundary Rivers, Lakes and Groundwaters
Second Assessment of Transboundary Rivers, Lakes and Groundwaters
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). October 2011
This Second Assessment of Transboundary Rivers, Lakes and Groundwaters provides a comprehensive, up-to-date overview of the status of transboundary waters in the European and Asian parts of the UNECE region. The Assessment presents an analysis of pressures, quantity and quality status, transboundary impacts, as well as responses and future trends of transboundary water resources in the region and highlights regional differences, specificities and vulnerabilities. Legal, institutional and socio-economic issues have a prominent place in this Second Assessment, given their crucial importance for transboundary water cooperation. The report aims to inform, guide and spur further action by national and local authorities, joint bodies and international and non-governmental organizations to improve the status of transboundary waters and related ecosystems.
River Basin Commissions and other Institutions for Transboundary Water Cooperation [ - 457.84 KB]
- 457.84 KB]
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). 2009
This publication analyses structures and activities of joint bodies and presents recommendations for strengthening transboundary water cooperation and establishing and improving joint bodies in Eastern Europe, Caucasus and Central Asia (EECCA) countries. It focuses particularly on aspects where existing joint bodies in EECCA countries could improve their activities by strengthening institutional mechanisms.
 Transboundary Flood Risk Management. Experiences from the UNECE region [
Transboundary Flood Risk Management. Experiences from the UNECE region [ - 4.74 MB]
- 4.74 MB]
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). 2009
This publication is based on the discussion and findings of the Workshop on Transboundary Flood Risk Management organized under the Water Convention in April 2009. It builds on the practical experience from 10 river basins in the UNECE region. The examples are offered as an analysis of concrete situations, problems encountered and progress made, as well as of remaining challenges and possible solutions. The publication aims to document practical experience, together with general conclusions, which can be applied throughout the region.
The Water Convention... at your service [ - 479.2 KB]
- 479.2 KB]
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). 2009
This brochure introduces the 1992 UNECE Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes.
 Our waters: joining hands across borders. First Assessment of Transboundary Rivers, Lakes and Groundwaters [
Our waters: joining hands across borders. First Assessment of Transboundary Rivers, Lakes and Groundwaters [ - 15.25 MB]
- 15.25 MB]
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). 2007
This publication describes the hydrological regime of 140 transboundary rivers and 30 transboundary lakes in the European and Asian parts of the region, as well as 70 transboundary aquifers located in South-Eastern Europe, Caucasus and Central Asia, as well as pressure factors in their basins, their status and transboundary impact, trends, future developments and envisaged management measures. Water sharing among riparian countries, increasing groundwater abstraction for agricultural purposes and drinking water supply, pollution from diffuse sources (e.g. agriculture, urban areas) as well as point sources (e.g. municipal sewage treatment and aging industrial installations), and the effects of climate change on water resources are among the many issues documented.
Transboundary River Basin Management in Europe. Thematic paper for Human Development Report 2006 [ - 94.06 KB]
- 94.06 KB]
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). 2006
This paper makes a review of the transboundary water resources management situation in Europe.
 Strategies for monitoring and assessment of transboundary rivers, lakes and groundwaters
Strategies for monitoring and assessment of transboundary rivers, lakes and groundwaters
[ - 1.38 MB]
- 1.38 MB]
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). 2006
This publication explains the key principles of and approaches to monitoring and assessment of transboundary watercourses and describes strategies for monitoring and assessing these watercourses. It highlights areas of interest to policy and decision makers and provides ground rules for water managers involved in or responsible for establishing and carrying out cooperation between riparian countries, as well as for representatives of joint bodies. The publication stresses the underlying legal, administrative and financial aspects of monitoring and assessment and discusses the constraints on and opportunities for cooperation. It draws on the experience gained with the implementation of pilot projects for transboundary rivers under the 1992 UNECE Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes (Water Convention) and proposes step-by-step approaches that take into account the available human and financial resources, particularly in countries with economies in transition.
 Rhine Case Study [
Rhine Case Study [ - 1.84 MB]
- 1.84 MB]
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), International Hydrological Programme (IHP), PCCP series. 2003
Experience with conflicts and cooperation in the Rhine basin proves the usefulness of river basin organizations. In this publication, the most important organizations are described, with their legal background, their tasks and duties, and their development. The theoretical aspects of conflict prevention and resolution are illustrated with water-related conflicts along the river Rhine. These cases deal with flooding, navigation, fisheries, water pollution, salt discharge, and accidental spills.
Protocol on Water and Health to the 1992 Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes [ - 44 KB]
- 44 KB]
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), World Health Organization (WHO). 1996
The objective of this Protocol is to promote at all appropriate levels, nationally as well as in transboundary and international contexts, the protection of human health and well-being, both individual and collective, within a framework of sustainable development, through improving water management, including the protection of water ecosystems, and through preventing, controlling and reducing water-related disease.
Convention on the protection and use of transboundary watercourses and international lakes [ - 43 KB]
- 43 KB]
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). 1992
The UNECE Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes (Water Convention) is intended to strengthen national measures for the protection and ecologically sound management of transboundary surface waters and groundwaters. The Convention obliges Parties to prevent, control and reduce water pollution from point and non-point sources. It also includes provisions for monitoring, research and development, consultations, warning and alarm systems, mutual assistance, institutional arrangements, and the exchange and protection of information, as well as public access to information.
"Fierce national competition over water resources has prompted fears that water issues contain the seeds of violent conflict. If all the world's peoples work together, a secure and sustainable water future can be ours."
Kofi Annan
Former UN Secretary-General

>> Groundwater. A border line case
International Groundwater Resources Assessment Centre (IGRAC) of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
Year: 2008
Duration: 4min47sec
This video addresses issues around transboundary aquifers. Interventions at one side of the border have impact on the other side of the border. Tensions rise where water is scarce. Examples of Kenya and Uganda are given. The video shows also some examples of cooperative solutions in India and emphasizes the importance of collecting, analyzing and sharing data.
Francesca Bernardini
Secretary of the Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes of UNECE Water Convention
Ms. Bernardini is coordinator of the UN-Water taskforce on Transboundary Waters. She is also the Co-Secretary of the Protocol on Water and Health which aims to protect human health and well-being by better management of water resources, with a focus and water supply and sanitation.
To request an interview, please send an email to Pilar González
>> Photo stories: World Water Day 2009. One Earth, Limited Resources: Sharing water across borders
Copyright | Terms of use | Privacy notice | Site Index | Fraud alert | Help